Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 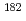 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Maeda, Makoto; Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(8), p.2995 - 2999, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1388 - 1398, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for  Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A
Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the
Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by
Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
 I(n,
I(n,  ) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactor
) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactorNakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.851 - 865, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study performed integral experiments of  I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of
I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of  I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from
I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from 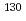 I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the
I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the 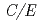 ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of
ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of  I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of
I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of  I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere
I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere  below 100 keV.
below 100 keV.
 Np(n,
Np(n,  ) reaction with TC-Pn in KUR
) reaction with TC-Pn in KURNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 93, 2022/07
In terms of nuclear transmutation studies of minor actinides in nuclear wastes, the present work selected  Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A
Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the
Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from  Pa in radiation equilibrium with
Pa in radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated
Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(10), p.1061 - 1070, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a well-thermalized neutron field, it is principally possible to drive a thermal-neutron capture cross-section without considering an epithermal neutron component. This was demonstrated by a neutron activation method using the graphite thermal column (TC-Pn) of the Kyoto University Research Reactor. First, in order to confirm that the graphite thermal column was a well-thermalized neutron field, neutron irradiation was performed with neutron flux monitors:  Au,
Au,  Co,
Co,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)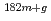 Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5
Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5 0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4
0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4 0.3 barn. The
0.3 barn. The  Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between
Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between  Au and
Au and  Mo monitors.
Mo monitors.
 Cf irradiator for delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy applications
Cf irradiator for delayed gamma-ray spectroscopy applicationsTohamy, M.*; Abbas, K.*; Nonneman, S.*; Rodriguez, D.; Rossi, F.
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 173, p.109694_1 - 109694_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Harada, Hideo
Applied Sciences (Internet), 11(14), p.6558_1 - 6558_20, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For accuracy improvement of neutron activation analysis and neutron capture cross section, bias effects are investigated on g- and s-factors in the Westcott convention. As origins of biases, a joining function shape, neutron temperature and sample temperature, have been investigated. Biases are quantitatively deduced for two 1/v isotopes ( Au,
Au,  Co) and six non-1/v isotopes (
Co) and six non-1/v isotopes ( Am,
Am,  Eu,
Eu, 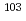 Rh,
Rh,  In,
In,  Hf,
Hf,  Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Harada, Masahide; Teshigawara, Makoto; Oi, Motoki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1000, p.165252_1 - 165252_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)This study explores high-energy neutron components of the extracted neutron beam at J-PARC pulsed neutron source using the foil activation method with threshold reactions. Foils of aluminum, gold, bismuth, niobium, and thulium were used to cover the neutron energy range from 0.3 MeV to 79.4 MeV. The experiment was performed using neutron beams of BL10 (NOBORU). The foils were irradiated by a neutron beam at 13.4 m from the moderator. To characterize high-energy neutron fields for irradiation applications, reaction rates in three different configurations with and without B C slit and Pb filter were examined. To compare the experiments with calculations given for the user, reaction rates for corresponding reactions were calculated by the PHITS code with the JENDL-3.2 and the JENDL dosimetry file. Although there was a systematic tendency in C/E (Calculation/Experiment) ratios for different threshold energies, which C/E ratio decreased as threshold energy increased up to 100 MeV, and all C/E ratios were in the range of 1.0
C slit and Pb filter were examined. To compare the experiments with calculations given for the user, reaction rates for corresponding reactions were calculated by the PHITS code with the JENDL-3.2 and the JENDL dosimetry file. Although there was a systematic tendency in C/E (Calculation/Experiment) ratios for different threshold energies, which C/E ratio decreased as threshold energy increased up to 100 MeV, and all C/E ratios were in the range of 1.0 0.2. This indicated that high-energy neutron calculations were adequate for the analysis of experimental data for NOBORU users.
0.2. This indicated that high-energy neutron calculations were adequate for the analysis of experimental data for NOBORU users.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)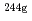 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)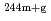 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)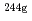 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)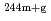 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
 for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protons
for a mercury target induced by 3-GeV protonsMatsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato*; Maekawa, Fujio
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 483, p.33 - 40, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)A thick target neutron yield for a mercury target at an angle of 180 from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
from the incident beam direction is measured with the time-of-flight method using a 3-GeV proton beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Comparing the experimental result with a Monte Carlo particle transport simulation by the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) shows that there are apparent discrepancies. We find that this trend is consistent with an experimental result of neutron-induced re- action rates obtained using indium and niobium activation foils. Comparing proton-induced neutron-production double-differential cross-sections for a lead target at backward directions between the PHITS calculation and experimental data suggests that the dis- crepancies for our experiments would be linked to the neutron production calculation around 3 GeV by the PHITS spallation model and/or the calculation of nonelastic cross-sections around 3 GeV in the particle transport simulation.
Harada, Hideo; Takayama, Naoki; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Physics Communications (Internet), 4(8), p.085004_1 - 085004_17, 2020/08
A new convention of epithermal neutron spectrum is formulated for improving accuracy of resonance integrals. The new type function is proposed as an approximating function of epithermal neutron spectrum based on calculations by the state-of-art Monte Carlo code MVP-3. Bias effects on determination of resonance integrals due to utilizing approximating functions of the traditional types and the new type are compared. The other bias effect is also investigated, which is caused by neglecting position dependence of a neutron spectrum inside an irradiation capsule. For demonstrating the bias effects due to these assumptions on neutron spectrum quantitatively in a practical case, the thermal neutron-capture cross section and resonance integral of  Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor
Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor  introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors (
introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.
Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.
 Am(n,
Am(n, )
)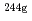 Am,
Am, 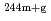 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 132, 2020/08
Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examinded by
Am was examinded by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by  -ray measurement.
-ray measurement.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.388 - 400, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section ( ) and resonance integral(I
) and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
) Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used
Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used  Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available
Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available  Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of
Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in a standard
Cs in a standard  Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify
Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify  Cs. The analyzed
Cs. The analyzed  Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the
Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the  , and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of
, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 8.57
values were derived as 8.57 0.25 barn, and 45.3
0.25 barn, and 45.3 3.2 barn, respectively. The
3.2 barn, respectively. The  obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3
obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3 0.3 barn.
0.3 barn.
Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Shibahara, Yuji*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 106, 2019/08
Under the ImPACT project, the neutron capture cross-section measurements of Cesium-135 ( Cs) among the long-lived fission products have been performed at Kyoto University. This paper reports measurements of the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Cs) among the long-lived fission products have been performed at Kyoto University. This paper reports measurements of the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Cs at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR).
Cs at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR).
Nakamura, Shoji; Kitatani, Fumito; Kimura, Atsushi; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.493 - 502, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section( )and resonance integral(I
)and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Np(n,
Np(n, )
) Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the
Np reaction by an activation method. A method with a Gadolinium filter, which is similar to the Cadmium difference method, was used to measure the  with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of
with paying attention to the first resonance at 0.489 eV of  Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A
Np, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as a cut-off energy. Neptunium-237 samples were irradiated at the pneumatic tube of the Kyoto University Research Reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as monitors to determine thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A  -ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of
-ray spectroscopy was used to measure activities of  Np,
Np,  Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Np and neutron monitors. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 186.9
values were derived as 186.9 6.2 barn, and 1009
6.2 barn, and 1009 90 barn, respectively.
90 barn, respectively.
Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Ikeda, Yujiro; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hanayama, Ryohei*; Kondo, Yasuharu*; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*
Reza Kenkyu, 46(11), p.634 - 640, 2018/11
Compact neutron sources have been used as various diagnostics such as a neutron diffraction, neutron resonant analysis, and neutron radiography. The developments of the neutron detectors are essential for all of these applications, while the techniques are strongly dependent on the neutron energy and the aim of the measurement. This paper reviews neutron detection techniques pertinent to promote compact neutron source uses. Along with general neutron detection systems with conventional counters for slow neutrons, we have highlighted detectors for high energy neutrons with high time resolution and high sensitivity which could be applied in a laser-driven compact neutron source.
Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Tobita, Hiroshi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/02
JAEA and EC/JRC are carrying out collaborative research to develop NDA techniques that can be utilized for quantification of high radioactive special nuclear materials such as spent fuel and next generation minor actinide fuels. In the research, reliability of neutron transport codes is important because it is utilized for design and development of a demonstration system of next-generation Differential Die-away (DDA) technique in JAEA. In order to evaluate the reliability, actual neutron flux distribution in a sample cavity was examined in PUNITA device using JRC type DDA technique and JAWAS-T device using JAEA type DDA technique, and then the measurement results were compared with the simulation results obtained by the neutron transport codes. The neutron flux distribution in the target matrix was also examined in the PUNITA and compared with the simulation results. We report on the measurement and simulation results of the neutron flux distribution and evaluation results of the reliability of the neutron transport codes.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsuda, Norihiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Harada, Masahide; Maekawa, Fujio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(10), p.1585 - 1594, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:85.7(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi; Shibahara, Yuji*; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Hori, Junichi*
KURRI Progress Report 2015, P. 67, 2016/08
The activation measurements of Np-237 were performed with neutron sources at KURRI-Linac. It was found that activation measurements supported the evaluated cross-section data of JENDL-4.0.